How much does the “right” hospital bed really affect outcomes, staff workload, and budget?
In simple terms, Manual Hospital Beds vs Electric Beds: Cost, Functionality, and Applications comes down to three things: how often positions need to change, how dependent patients are, and how much time your team can spend on bed adjustments.
This guide explains the types, Hospital Bed Cost Comparison, daily-use differences, safety standards, and real buying mistakes—so you can choose confidently with trust medi.
What Are Manual And Electric Hospital Beds?
Hospital beds are Adjustable Hospital Beds built to support clinical care: backrest elevation, knee/leg positioning, and height adjustment (depending on model). They’re part of Hospital Furniture Beds planning because they affect nursing time, fall risk controls, patient comfort, and even room workflow.
At a high level:
- Manual Hospital Beds: adjustments are done using hand cranks and mechanical linkages.
- Electric Hospital Beds: adjustments are done using powered actuators (motors) and a handset/controls.
Both categories can share core Hospital Bed Features like side rails, braking casters, IV pole provisions, and mattress platform sections—yet their operation and total ownership cost are very different.
Why Comparing Manual Hospital Beds vs Electric Beds Is Important?
Buying beds isn’t just a line item. It shapes daily operations for years.
A clear comparison helps you:
- Match Patient Bed Types to patient acuity (general wards vs ICU).
- Predict staffing impact (manual cranking vs powered adjustments).
- Avoid hidden costs: downtime, parts availability, training, and service contracts.
- Meet safety expectations tied to bed systems and rails—an area where regulators have long tracked entrapment and injury risks. (fda.gov)
If your facility is expanding (or replacing aging inventory), a structured choice also helps you negotiate better with a Hospital Bed Supplier and validate Medical Bed Specifications before signing.
What Is A Manual Hospital Bed?
A manual model is a mechanically adjustable bed where staff use cranks to change:
- Backrest angle
- Knee/leg section
- (Sometimes) bed height, depending on design
Strengths:
- Lower upfront price
- No reliance on power for adjustments
- Often simpler troubleshooting
Trade-offs:
- More physical effort for staff
- Slower repositioning
- Less convenient for frequent micro-adjustments (common in long stays)
From a regulatory standpoint, manual beds can still fall under FDA product categories such as “manual adjustable hospital bed.” (FDA Access Data)
What Is An Electric Hospital Bed?
An electric model uses motors/actuators to adjust sections and (commonly) height, controlled by handset, integrated side-rail controls, or nurse panels depending on the configuration.
Strengths:
- Faster, easier repositioning (especially for heavier or dependent patients)
- More precise positioning for comfort, respiratory support, and nursing tasks
- Better fit for frequent adjustments (pain control, edema management, mobility protocols)
Trade-offs:
- Higher purchase price
- More complex components (motors, controls, cables)
- Requires reliable maintenance support and parts availability
Electric beds still must meet safety expectations for medical beds, including standards used internationally for essential performance and safety of medical beds. (ISO)
Cost Comparison Between Manual And Electric Hospital Beds
There is no single global price—brand, load rating, mattress platform, rail system, and local market all change the quote. Still, you can plan with realistic bands.
Typical pricing bands (planning level)
- Manual beds are commonly in a lower entry band. Some market references place manual ranges in the hundreds to low thousands per unit depending on features.
- Electric beds often start higher and climb quickly as you move from basic electric to advanced ICU-grade configurations. Consumer-facing guidance for hospital beds in general shows a wide range driven by features, with electric models typically costing more. (GoodRx)
Total cost of ownership (TCO) is where facilities feel it
Beyond purchase price, include:
- Preventive maintenance and inspections
- Spare parts lead time
- Downtime cost (bed out of service)
- Staff time saved or lost during repositioning routines
- Training and onboarding time
If you’re comparing offers from any Hospital Bed Manufacturer, request a simple 5-year cost view: estimated parts, labor assumptions, and response-time commitments.
Quick Hospital Bed Cost Comparison table
| Line Item | Manual Hospital Beds | Electric Hospital Beds |
| Upfront purchase | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance complexity | Mostly mechanical | Electrical + mechanical |
| Downtime impact | Often easier fixes | Can require specialist service |
| Staff effort per adjustment | Higher | Lower |
| Best value when… | Positions change occasionally | Positions change frequently |
Functionality Differences Between Manual And Electric Beds
This is the heart of Hospital Bed Functionality.
Manual functionality: dependable basics
Manual beds typically cover the “must-have” angles for many general patients. If care plans don’t require constant repositioning, manual operation can be perfectly workable.
Electric functionality: speed + precision
Electric beds excel when you need frequent repositioning (short cycles), fine angle control, and easy height changes to support:
- safer transfers
- wound prevention routines
- respiratory positioning
- staff ergonomics
When reviewing Medical Bed Specifications, compare these points line by line:
- number of powered functions (back, knee, height, tilt if applicable)
- max safe working load
- minimum/maximum height range
- rail design compatibility with mattress thickness
- control lockout features (especially for confusion risk)
- caster quality and braking system
Applications Of Manual Hospital Beds In Clinics And Hospitals
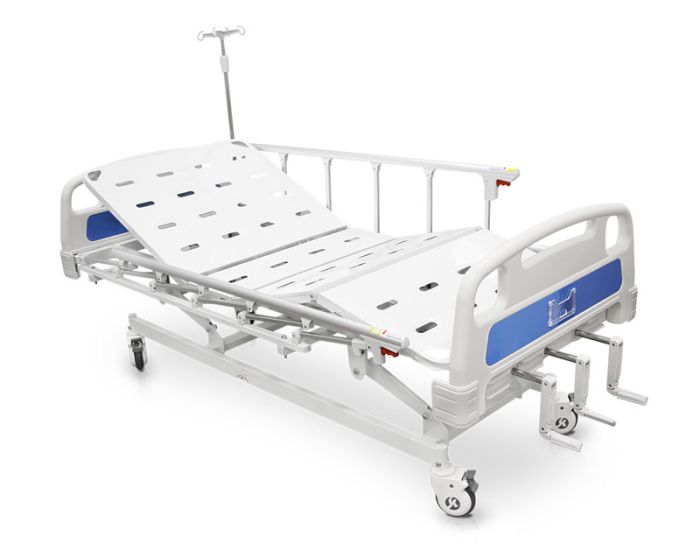

Manual models can be a smart fit for Hospital Beds For Clinics and selected areas in hospitals where acuity is moderate and budget needs discipline.
Common Hospital Bed Applications for manual beds:
- outpatient recovery rooms with short stays
- step-down areas with stable patients
- small hospitals needing reliable core inventory
- emergency overflow rooms (when speed of deployment matters)
- facilities where power reliability is inconsistent
They also work well when the facility has strong manual-handling protocols and patient dependence is limited. Many providers include manual beds as part of broader Healthcare Bed Solutions to balance spending across departments.
Applications Of Electric Hospital Beds In Hospitals And ICUs
Electric beds are usually the default choice for higher-acuity settings because they reduce friction in care.
Typical Hospital Beds For Hospitals use cases:
- medical/surgical wards with higher turnover and frequent position changes
- post-op units where comfort and transfer safety matter
- long-stay departments where repositioning routines are intensive
ICU-focused use cases:
- frequent posture changes for oxygenation strategies
- rapid height changes for procedures and transfers
- easier patient handling for sedated or dependent patients
If you’re equipping critical care, don’t treat “electric” as one level. Ask your Hospital Bed Supplier to separate basic electric, advanced electric, and ICU-specific configurations, then map them to your clinical workflow.
Patient Comfort And Care Considerations
Patient comfort is not “luxury.” It reduces complaints, improves cooperation with care, and supports rest.
Consider:
- Can the patient adjust position independently? Electric controls can help for suitable patients, while lockout prevents misuse in others.
- How often does staff need to change angles? Manual cranking can become a pain point during busy shifts.
- Does the bed support safe entry/exit? Height range matters as much as backrest movement.
Also, rails must be chosen carefully. The FDA has documented hundreds of bed-rail entrapment reports over the years and stresses assessment, correct pairing of mattress/rail/bed system, and ongoing monitoring. (fda.gov)
Maintenance And Durability Factors
Durability is not only frame strength—it’s the weakest repeated-use component.
Manual beds: wear points
- crank mechanisms
- linkages and joints
- bushings, fasteners
- caster assemblies
Electric beds: more to monitor
- actuators and motors
- handsets, control panels, cables
- battery backup (if included)
- control lockouts and fault codes
Practical tip: whichever type you buy, confirm your parts pipeline. A bed that “lasts” but can’t get spare actuators or rail latches quickly becomes a workflow problem.
Safety Standards For Hospital Beds
Most facilities evaluate safety through a mix of national regulations and widely used technical standards.
Key references you’ll hear in procurement:
- IEC 60601-2-52: a widely referenced standard covering basic safety and essential performance for medical beds. (ISO)
- Bed-rail entrapment risk guidance and dimensional considerations promoted through FDA resources and the Hospital Bed Safety Workgroup. (fda.gov)
What to request from a vendor (manual or electric):
- Documentation aligning bed system + mattress + rails as a safe combination
- Clear safe working load and intended patient population
- Instructions for cleaning, disinfection compatibility, and inspection intervals
- Evidence of quality management and traceability (especially if you’re standardizing across departments)
Which Hospital Bed Type Is Best For Your Facility?
A practical way to decide is to segment by patient dependency and adjustment frequency.
Use Manual Hospital Beds when:
- patient acuity is lower
- repositioning is occasional
- budget must cover more rooms quickly
- you want simple, mechanical dependability
Use Electric Hospital Beds when:
- patients need frequent changes
- staffing strain is real
- safe transfers and height control are priorities
- comfort and independent adjustment matter
Many hospitals mix both: manual beds in lower-acuity zones, electric beds in wards with heavier workload, and advanced electric systems in ICU. That mix often produces the best cost control without sacrificing care quality.
Budget Vs Performance Considerations
Instead of “cheap vs expensive,” think “where does performance pay for itself?”
Electric beds may justify cost when they:
- reduce staff time per repositioning cycle
- lower strain risk during adjustments
- shorten transfer time
- support protocols that require frequent positioning changes
Manual beds may win when:
- patient needs are stable
- your facility prioritizes coverage volume
- maintenance teams want maximum simplicity
Your best purchasing argument is a short model: number of adjustments per patient per day × staff minutes saved × bed count. Even if you don’t convert it to currency, it makes the decision clear.
Common Mistakes When Choosing Hospital Beds
- Buying based on price only, then discovering the bed height range doesn’t support safe transfers.
- Ignoring mattress and rail compatibility—this is tied to entrapment risk. (fda.gov)
- Not checking parts lead time and service coverage (especially for electric actuators).
- Choosing one bed type for every department without matching actual patient mix.
- Skipping a small pilot rollout and staff feedback before a large order.
FAQ About Manual And Electric Hospital Beds
1) Are electric beds always better than manual beds?
Not always. Electric beds are better when adjustments are frequent or patients are more dependent. Manual beds can be the smarter purchase for stable patients and controlled budgets.
2) What functions should I prioritize first?
Start with height range, braking stability, and backrest/knee adjustments. Then decide whether powered height and powered sections are required for your workflow.
3) Do bed rails automatically make a bed safer?
No. Rails can reduce some fall risks, but incorrect use or poor fit can increase entrapment risk. Facilities should assess each patient and ensure the bed system components match correctly. (fda.gov)
4) How do I compare quotes from more than one Hospital Bed Manufacturer?
Ask each supplier to provide the same checklist: functions, load rating, minimum height, rail type, mattress compatibility, warranty, spare parts availability, and service response time. That keeps comparisons fair.
5) Can clinics use electric beds, or is that only for hospitals?
Clinics can use electric models when they handle more dependent patients, post-op recovery, or longer observation. Many facilities mix types across rooms.
Choosing between Manual Hospital Beds and Electric Hospital Beds becomes easy when you match the bed to patient needs, staff workload, and safety requirements—not just the purchase price. Manual beds can cover essential care reliably, while electric beds deliver faster positioning, better ergonomics, and stronger support for high-acuity workflows.
If you want a tailored recommendation, spec sheet review, or a quote built around your departments and patient mix, trust medi can help you select the right Healthcare Bed Solutions and supply the most suitable hospital bed configuration for your facility.

