Ever watched a nurse adjust a patient’s position five times in one hour—and wished the bed could do half the work? That’s exactly why Electric Hospital Beds: Features, Benefits, and Use Cases in Modern Hospitals has become a practical buying topic, not a “nice-to-have.”
Electric hospital beds use powered actuators and simple controls to change height, backrest, and leg positions safely and fast—supporting comfort, treatment, and staff workflow.
In this guide, you’ll learn what these beds are, key hospital bed features, types, safety standards, real use cases, and how to choose the right model with trust medi.
What Are Electric Hospital Beds?
Electric Hospital Beds (also called Motorized Hospital Beds or Electric Medical Beds) are patient beds that adjust using electric motors instead of manual cranks. Common movements include:
- Bed height up/down (helps safe transfers and caregiver ergonomics)
- Backrest (Fowler/semi-Fowler positioning)
- Leg/knee raise (reduces sliding and supports circulation)
- Trendelenburg / reverse Trendelenburg (depending on model)
- Chair or cardiac chair position (on advanced designs)
These are a core part of modern Hospital Furniture Beds because they support both clinical care and operational efficiency—especially when patient acuity is high.
Why Modern Hospitals Prefer Electric Hospital Beds?
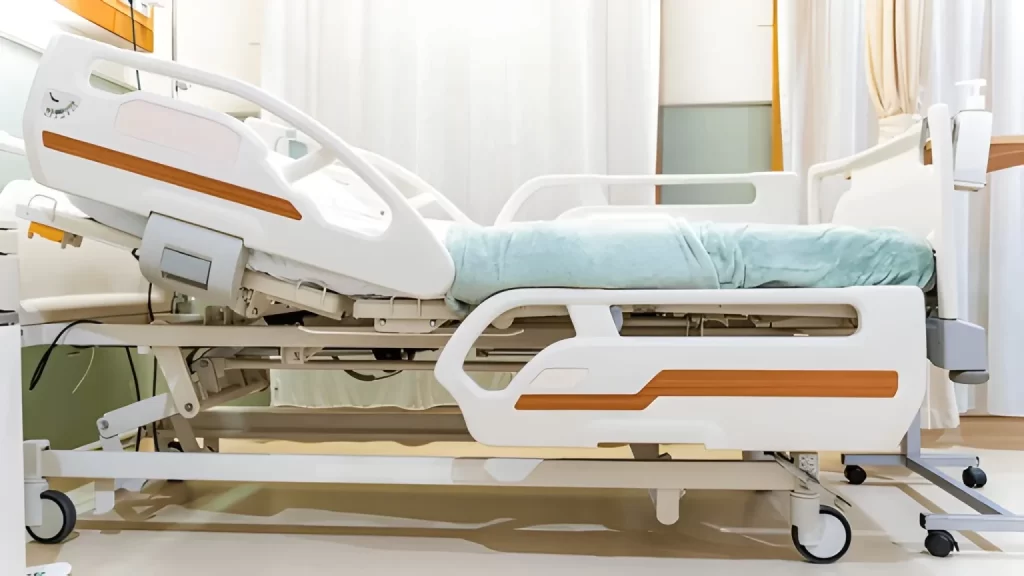
Hospitals lean toward Adjustable Hospital Beds for day-to-day reasons that show up on every ward:
- Fewer manual handling tasks: Powered adjustment reduces repeated physical effort during repositioning, linen changes, wound care, and transfers.
- More consistent positioning: Staff can set angles and heights quickly, which matters for respiratory comfort, feeding, and post-op recovery.
- Fall-risk routines are easier to follow: Low-height modes and quick height changes help teams keep safer bed setups during rounds. Patient falls are widely recognized as a frequent hospital adverse event, with reported ranges around 3–5 falls per 1,000 bed-days and over one-third resulting in injury. (World Health Organization)
- Better readiness for “busy hours”: When admissions spike, powered beds speed up bed turnover and room prep.
Key Features Of Electric Hospital Beds
When buyers compare Hospital Bed Functions, they usually focus on comfort first—then realize controls, safety, and serviceability matter just as much. Here are the most important Hospital Bed Features to evaluate.
Core adjustment functions
- Height adjustment (minimum and maximum height)
- Backrest angle range
- Knee/leg section articulation
- Trendelenburg / reverse Trendelenburg (if required by your clinical protocols)
Controls and usability
- Hand pendant or integrated side-rail controls (Hospital Bed Controls)
- Lockout functions (prevent unintended movement)
- Clear icons and tactile buttons for staff speed
Patient safety elements
- Side rails designed to reduce entrapment risk
- Auto-contour or anti-shear movements (helps reduce sliding and skin stress)
- Brake systems (central locking, directional caster option)
- Battery backup for power interruptions
Regulators and safety bodies emphasize entrapment risk controls around rails, mattresses, and accessories. FDA materials describe seven entrapment zones and recommend facilities inventory bed systems and accessories to reduce risk. (fda.gov)
Materials and infection control
- Seamless surfaces where possible
- Resistant coatings and easy-clean geometry
- Compatibility with hospital-grade disinfectants
Smart add-ons (optional)
Many facilities now ask about Smart Hospital Beds as part of broader Healthcare Bed Solutions:
- Bed-exit alarms and patient movement alerts
- Nurse call integration
- Weighing scales and data connectivity (model-dependent)
Types Of Electric Hospital Beds
Not every Electric Bed For Hospitals is an ICU bed, and not every clinic needs ICU-grade complexity. Typical categories include:
- General ward Electric Hospital Beds
Daily inpatient use with standard height/back/leg functions. - ICU Electric Beds
Higher-duty frames, wider feature sets, advanced positioning, better accessory integration, and often more robust side-rail designs. - Bariatric electric beds
Higher safe working load, reinforced deck, wider surface. - Pediatric electric beds
Sizes and rail designs tailored for pediatric safety requirements (varies by market). - Electric Bed For Clinics
Often simpler, focused on examination, short stays, or day procedures—still motorized, but with fewer advanced positioning modes.
Benefits For Patients And Medical Staff
Electric beds are not just “more comfortable.” They change daily workflows in ways you can feel in staffing, safety routines, and patient experience.
Benefits for patients
- Easier position changes for comfort and breathing
- Better support for feeding and recovery positioning
- Safer transfer setup when the bed height is optimized
- Reduced “sliding down the bed” when knee sections and contouring are used correctly
Benefits for staff
- Faster positioning for care tasks (dressing changes, respiratory support, line checks)
- Less repetitive pushing/pulling during manual cranking
- Improved standardization: when every unit has similar Hospital Bed Controls, training is easier
A practical note: falls remain a major patient safety concern. WHO highlights patient falls as a common adverse event and reports typical hospital fall rates in the 3–5 per 1,000 bed-days range, with a significant portion causing injury. (World Health Organization)
Use Cases Of Electric Hospital Beds In Hospitals
Here’s where Patient Care Beds earn their keep in modern facilities:
- Post-operative recovery: semi-Fowler positioning, easier pain management positioning, and transfer support
- Internal medicine wards: comfort, mobility support, pressure-relief routines
- Orthopedics: easier leg elevation and safer bed height for physiotherapy sessions
- Maternity and women’s health (non-delivery): positioning and caregiver access
- Longer stays and geriatric care: low-height setups, bed-exit alerts (if available), and frequent repositioning support
Quick mapping table (bed function → typical use)
| Hospital bed function | Most common clinical use |
| Height up/down | Transfers, fall-risk routines, caregiver ergonomics |
| Backrest elevation | Feeding, respiratory comfort, post-op recovery |
| Knee/leg raise | Comfort, reduced sliding, circulation support |
| Trendelenburg modes | Selected clinical positioning needs (protocol-based) |
| Bed-exit alarm (smart) | Fall-risk monitoring, night-time observation |
Electric Beds In ICUs And Critical Care Units
In ICU settings, bed capabilities can directly impact speed and safety during critical moments. ICU Electric Beds usually prioritize:
- Rapid positioning changes (including higher backrest angles and chair positioning)
- Robust accessory mounting (poles, pumps, ventilator circuit management accessories)
- Stable frames and higher-duty casters for transport inside the unit
- Better integration options (depending on hospital infrastructure)
Also, ICU patients face higher skin injury risk and mobility limitations, so consistent positioning and easier staff workflows matter a lot. Many ICU teams also prefer beds with clearer lockouts and status indicators to prevent unintended movement.
Safety Standards For Electric Hospital Beds
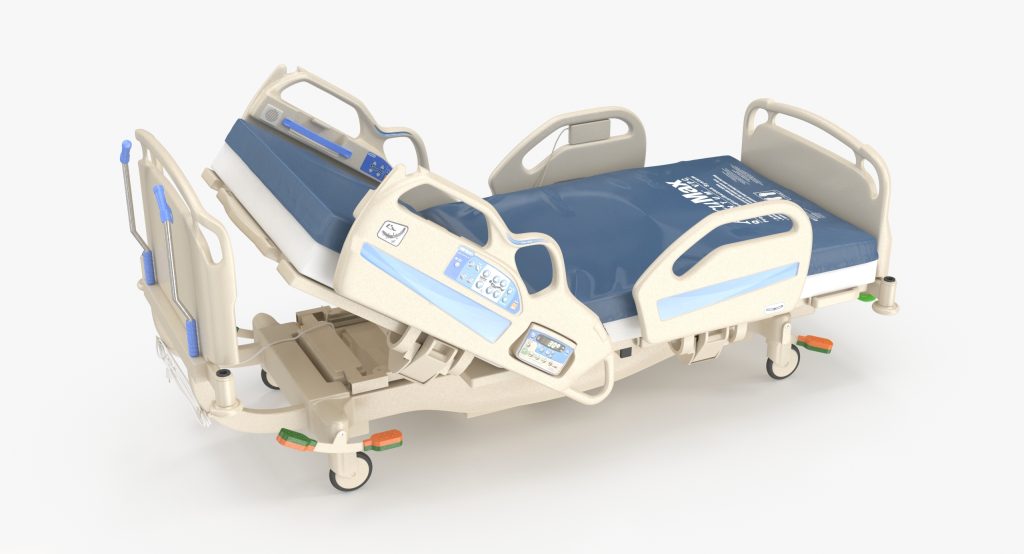
Buying decisions should include documented compliance, not just brochure claims.
Key standards and guidance to know
- IEC 60601-2-52: a widely referenced international standard for the basic safety and essential performance of medical beds for adults. (ISO)
- FDA bed entrapment guidance: focuses on reducing entrapment risk and describes entrapment zones and mitigation strategies involving rails, mattresses, and accessories. (fda.gov)
- Some national regulators (for example, Health Canada) also publish guidance describing entrapment zones and hazards to consider in adult hospital beds. (Canada)
What to request from a Hospital Bed Manufacturer
Ask your Hospital Bed Manufacturer for:
- Compliance documentation (test reports/certificates where applicable)
- Clear safe working load and patient weight limits
- Entrapment risk guidance for the exact rail + mattress combinations you plan to use
- Cleaning and chemical compatibility guidance
Maintenance And Durability Considerations
Electric beds pay off when they stay reliable. Maintenance planning should be part of the purchase, not an afterthought.
Practical maintenance checklist
- Actuators and moving joints: check unusual noises, slower lift speed, uneven movement
- Battery health: verify runtime and replacement intervals
- Caster and brake wear: worn brakes cause real safety incidents
- Controls and cables: inspect for damage, fluid ingress, loose connectors
- Surface integrity: chipped paint and cracked plastics become infection-control issues
Durability buying tip
If you’re comparing models, ask for:
- MTBF/service history (if available)
- Spare parts availability timeline
- Local service coverage and training
- Warranty terms that actually match your usage intensity (ICU ≠ low-traffic ward)
Electric Hospital Beds Vs Manual Beds
Manual beds still exist for cost-sensitive or low-acuity settings, but the trade-offs are clear.
Electric Hospital Beds
- Faster adjustments
- Less staff effort
- Better standard positioning routines
- More features and accessory options
Manual beds
- Lower upfront cost
- Fewer electronic parts
- Slower workflows and more physical effort
- Limited advanced positioning options
A good approach: keep manual beds for very specific low-acuity areas, and standardize electric beds where transfers, monitoring, and frequent repositioning are routine.
Cost Factors Of Electric Hospital Beds
Prices vary widely because the “bed” is really a system. Main cost drivers:
- Function set: basic vs advanced articulation, Trendelenburg, chair positions
- Duty level: general ward vs ICU Electric Beds frames, casters, and load ratings
- Smart features: sensors, alarms, connectivity (Smart Hospital Beds)
- Mattress and rails: not accessories—these are safety-critical components
- Service package: warranty length, spare parts, local technical coverage
- Compliance/testing requirements: documentation and certification scope
When evaluating total cost, include preventive maintenance, parts, and downtime risk—not only purchase price.
How To Choose The Right Electric Hospital Bed
Use a simple, repeatable process across departments.
Step-by-step selection method
- Define the clinical use: ward, step-down, ICU, short-stay clinic, bariatric needs
- List must-have functions: height range, backrest range, lockouts, rails, battery backup
- Confirm safety documentation: IEC 60601-2-52 alignment and entrapment guidance for the full bed system (bed + rails + mattress + accessories). (ISO)
- Run a hands-on trial: nurses and biomedical teams should test controls and maneuverability
- Plan fleet standardization: fewer variants make training and maintenance easier
- Verify after-sales support: parts availability, response times, training, PM schedules
Mini procurement checklist (print-friendly)
- Safe working load and warranty
- Bed height minimum (for fall-risk routines)
- Rail design + mattress compatibility guidance
- Brake quality and caster performance
- Cleaning compatibility documentation
- Service coverage and spare parts lead time
Common Mistakes When Buying Electric Hospital Beds
These are expensive errors that show up later in incident reviews and maintenance logs:
- Buying beds without confirming rail + mattress compatibility (entrapment risk) (fda.gov)
- Choosing “too many features” for the unit, which leads to staff avoiding functions
- Ignoring minimum bed height and brake quality (big impact on fall prevention routines) (World Health Organization)
- Underestimating service needs (no local parts, slow repair turnaround)
- Treating mattresses and rails as optional add-ons instead of system-critical components
FAQ About Electric Hospital Beds
1) Are Electric Hospital Beds worth it for non-ICU wards?
Often yes, because daily repositioning, transfers, and workflow speed matter on general wards—not only in critical care.
2) What’s the difference between Motorized Hospital Beds and Adjustable Hospital Beds?
In practice, the terms overlap. “Motorized” highlights powered movement; “adjustable” describes the outcome. Many buyers use both terms for the same category.
3) Do Smart Hospital Beds replace fall-prevention protocols?
No. Sensors and alarms help, but hospitals still need rounding routines, low-bed setups, and patient-specific risk plans. WHO notes falls are a frequent adverse event in hospitals. (World Health Organization)
4) What safety standard should we look for first?
IEC 60601-2-52 is a key reference for adult medical beds’ safety and performance. Also review regulator guidance on entrapment risks and accessories. (ISO)
5) Can we mix mattresses and rails across brands?
Sometimes, but it must be validated. FDA guidance stresses evaluating the whole bed system, including accessories and mattress fit, to reduce entrapment risk. (fda.gov)
Electric beds are now the workhorse of inpatient care: faster positioning, safer transfers, better daily comfort, and smoother staff routines. When you evaluate Electric Bed For Hospitals purchases, focus on the full system—functions, Hospital Bed Controls, rail and mattress safety, standards, and service support—not just the spec sheet.
If your facility is planning new Hospital Furniture Beds or upgrading Patient Care Beds, trust medi can help you shortlist the right Healthcare Bed Solutions, compare options by unit type, and align your purchase with safety guidance and long-term maintenance needs.

