Choosing a hospital bed sounds simple until you’re balancing patient safety, nursing workload, infection control, and budget. That’s why Hospital Bed Types Explained: Manual vs Electric vs ICU Beds matters for anyone buying beds for real clinical use.
A hospital bed is more than a frame and mattress. It’s a daily-use tool that affects comfort, mobility, pressure care, and staff efficiency.
In this article, you’ll learn the main Hospital Bed Types, how each one fits different patients and settings, and what to check before you buy by trust medi.
What Are Hospital Bed Types?
Hospital Bed Types usually fall into three practical groups based on how they move and what care level they support:
- Manual Hospital Beds: adjusted by hand cranks (backrest, leg section, sometimes height).
- Electric Hospital Beds: motorized adjustments controlled by handset or panel.
- ICU Hospital Beds: advanced electric beds built for critical care workflows and monitoring.
You may also hear “Patient Bed Types” used in tenders, which can include specialty variants like bariatric beds, pediatric beds, low beds (fall-risk), or long-term care beds. For hospitals and procurement teams, it’s best to classify beds by care level and function first, then add specialty needs.
Why Choosing The Right Hospital Bed Is Important?
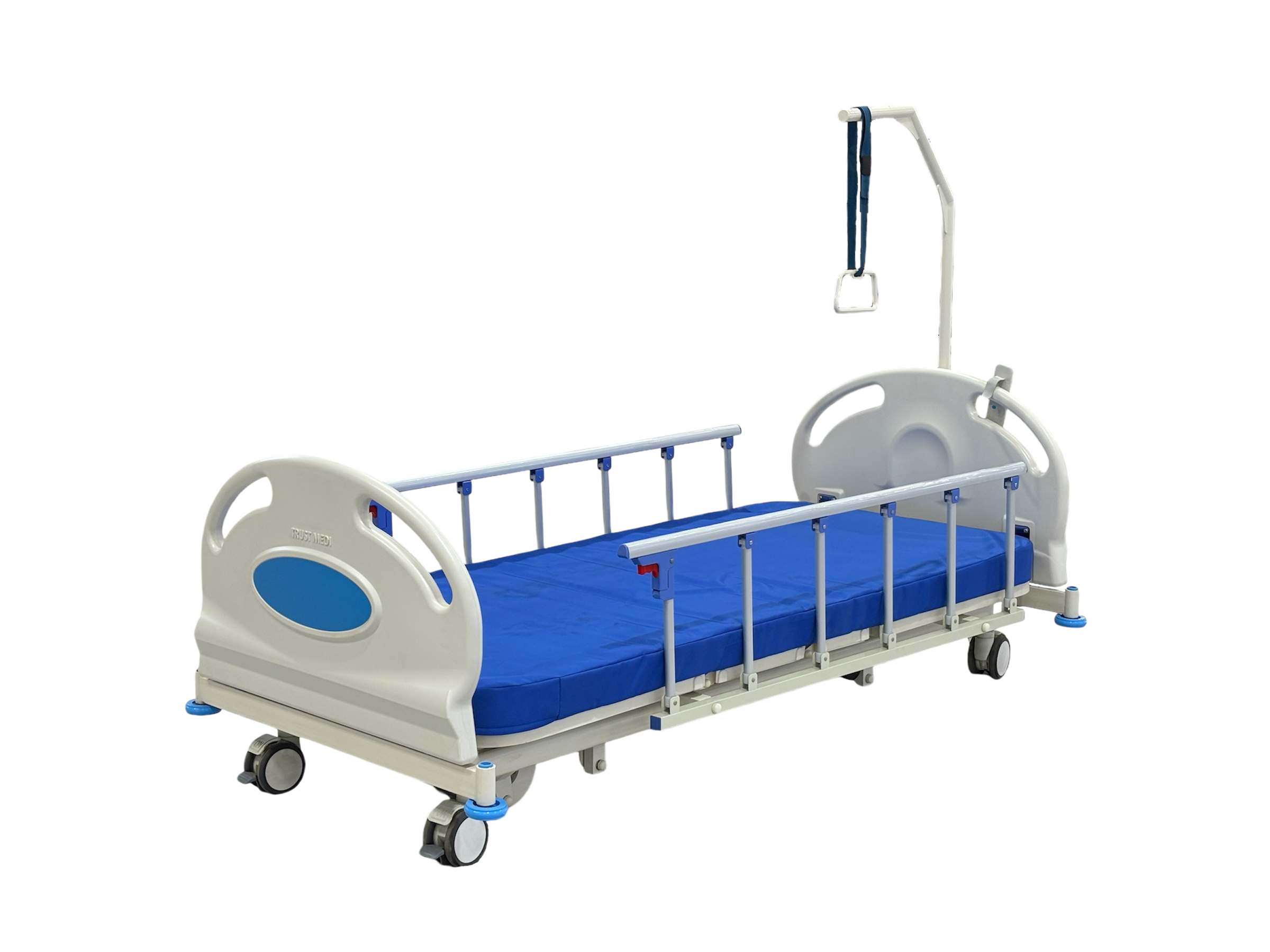
Beds are used 24/7, cleaned frequently, and adjusted dozens of times per dayso the wrong choice shows up fast.
Here’s what a “right” bed influences:
- Fall risk and safe transfers: Bed height and stability affect how safely patients get in and out. Research and hospital guidance often connect bed height and mobility to fall prevention efforts.
- Entrapment and side-rail safety: Poor rail design or wrong mattress pairing can create dangerous gaps. Regulators provide guidance to reduce entrapment hazards.
- Nursing workload: If staff must crank beds repeatedly, fatigue and time loss are realespecially in high-acuity units.
- Patient comfort and pressure care routines: Position changes and angles matter for breathing comfort, feeding, and skin care plans.
- Lifecycle cost: Cheaper beds can cost more through repairs, downtime, and spare parts issues.
This is why hospital beds sit inside broader Healthcare Bed Solutions and Hospital Furniture Beds planning, not just “a furniture purchase.”
What Is A Manual Hospital Bed?
A manual bed is a hospital bed where key positions are adjusted mechanicallyusually with one or more hand cranks. Some models offer:
- Backrest adjustment
- Knee/leg section adjustment
- Height adjustment (not always included)
Manual beds are common when power access is limited, budgets are tight, or patients don’t need frequent repositioning.
Features And Use Cases Of Manual Hospital Beds
Typical Hospital Bed Features in manual models:
- Simple mechanical articulation (fewer electronics to service)
- Basic side rails (varies by model)
- Fixed or limited height range on lower-cost units
- Standard caster system with brakes
Best-fit use cases:
- General wards with stable patients
- Short-stay observation (where staff can manage cranks)
- Backup inventory for surge capacity
- Smaller facilities that need reliable basics
Where manual beds struggle:
- High-turnover units needing frequent height changes
- Bariatric or high-dependency patients requiring regular repositioning
- Facilities aiming to reduce staff strain
If you’re comparing Patient Bed Types for mixed use, manual can be practical as a “base layer,” but it’s rarely the best choice for high-acuity care.
What Is An Electric Hospital Bed?
Electric Hospital Beds use motors to adjust bed positions with a handset, pendant, or integrated controls. Most electric beds offer:
- Backrest up/down
- Knee/leg section up/down
- Height up/down
- Trendelenburg / reverse Trendelenburg (depending on model)
Many facilities prefer electric beds because repositioning becomes quicker and less physically demanding for staff.
Benefits And Applications Of Electric Hospital Beds
Core Hospital Bed Functions that get easier with electric systems:
- Frequent repositioning for comfort and care routines
- Safer transfers via height adjustment
- Faster nursing workflows during rounds
Common settings:
- Medical-surgical wards
- Maternity units (depending on local practice and bed type)
- Post-op recovery areas
- Long-stay patient rooms where comfort matters daily
Electric models also overlap with Adjustable Hospital Beds in how buyers describe them. In procurement specs, be precise: define which sections are adjustable, the height range, and whether the bed has tilt functions.
One more point: because electric beds are medical electrical equipment, safety standards become more relevant. For adult medical beds, IEC 60601-2-52 is widely referenced for safety and essential performance requirements. (ISO)
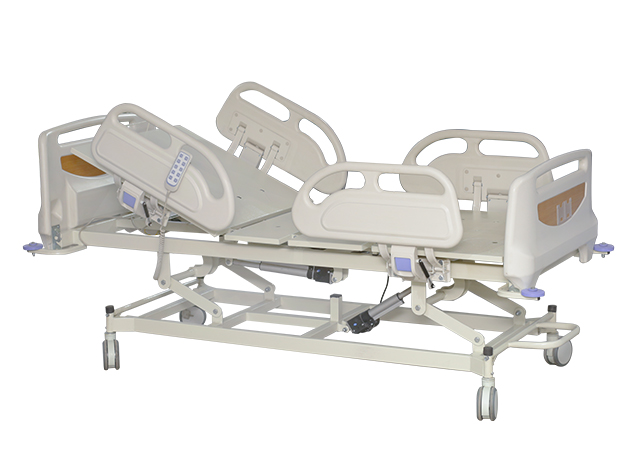
What Is An ICU Hospital Bed?
ICU Hospital Beds are advanced electric beds built for critical care demands. They typically support:
- Complex positioning and micro-adjustments
- Higher load ratings (varies by model)
- Integration with accessories (vents, monitors, pumps)
- Features that support respiratory care, turning protocols, and rapid access in emergencies
These beds are designed for high-risk patients where small positioning changes can matter a lot.
Key Features Of ICU Hospital Beds
Typical ICU-grade Hospital Bed Features include:
- Wider height range (including very low positions for fall-risk protocols)
- Advanced side-rail systems designed with entrapment risk in mind
- CPR quick-release (mechanical or electronic) for rapid flat positioning
- Built-in scale (on some models)
- Bed exit alarms / patient monitoring options (model dependent)
- X-ray cassette compatibility (some models)
- Better accessory mounting for ICU workflows
Entrapment safety is a serious topic in bed systems. Regulatory guidance focuses on reducing life-threatening entrapment hazards and identifies risk areas and dimensional criteria around rails, mattress interfaces, and openings.
Manual vs Electric vs ICU Beds Comparison
Here’s a practical comparison buyers can use during evaluation:
- Adjustment method
- Manual: hand cranks
- Electric: motors + handset
- ICU: advanced motors + expanded functions
- Best for
- Manual: low-acuity, limited repositioning
- Electric: general inpatient care, frequent adjustments
- ICU: critical care, high dependency patients
- Staff workload
- Manual: higher physical effort
- Electric: reduced effort, faster routines
- ICU: lowest effort with specialized controls
- Safety and risk management
- Manual: depends heavily on rail design and procedures
- Electric: better positioning control; still needs rail/mattress matching
- ICU: typically strongest set of safety-focused features (still depends on model)
- Cost
- Manual: lowest upfront
- Electric: mid-range
- ICU: highest upfront, often best fit for critical workflows
Which Hospital Bed Type Is Best For Hospitals And Clinics?
It depends on your patient mix, staffing, and how often beds are repositioned.
For hospitals (inpatient wards):
- A blend often works best: electric beds for most wards, ICU beds for critical care, and a smaller pool of manual beds for backup and low-acuity use.
- If your project is primarily Hospital Bed For Hospitals, standardization mattersfewer models make training, spares, and maintenance easier.
For clinics:
- Many clinics don’t need full inpatient beds, but some do (day surgery, recovery, observation, dialysis, specialty centers).
- If you need Hospital Bed For Clinics, electric models usually make more sense than manual because clinics rely on fast turnover and safe transfers with limited staff per patient.
A reliable Hospital Bed Supplier should help you map bed types to departments rather than pushing one model for everything.
Hospital Bed Specifications And Safety Standards
When tendering, define your Medical Bed Specifications clearly so suppliers can’t substitute lower-grade options.
Key specifications to include:
- Safe working load and patient weight limit
- Mattress platform dimensions and mattress compatibility rules
- Height range (minimum and maximum)
- Backrest and knee angle ranges
- Tilt functions (if needed): Trendelenburg/reverse
- Caster size, brake type, steering function
- Side rail type and latching reliability
- Cleaning compatibility (chemicals, contact times)
On safety standards:
- IEC 60601-2-52 is commonly referenced for adult medical beds’ basic safety and essential performance.
- Entrapment risk is addressed through guidance that identifies hazardous openings and recommends dimensional criteria for bed systems and accessories.
Also include documentation requirements (manuals, spare parts list, warranty terms, service network). For large purchases, ask for proof of conformity and test evidence aligned to the standards your facility requires.
Factors Affecting Hospital Bed Selection
A realistic selection checklist (the stuff that actually decides satisfaction after delivery):
- Patient acuity and mobility
- High dependency patients usually justify electric or ICU beds.
- Nurse-to-patient ratio
- Lower staffing capacity increases the value of motorized repositioning.
- Room size and layout
- Check turning radius, side clearance, and headwall equipment.
- Cleaning intensity
- Choose finishes and designs that survive frequent disinfection without peeling or cracking.
- Power and backup readiness
- Electric and ICU beds need reliable power planning (and sometimes battery backup).
- Service and spare parts
- A bed is only “high quality” if you can keep it running.
- Standardization goals
- Too many models create training and spare parts chaos.
Your choice of Hospital Bed Manufacturer matters here, not just the model namebuild quality and long-term support vary widely.
Common Mistakes When Choosing Hospital Beds
These show up again and again in hospital projects:
- Buying on brochure features instead of clinical workflow
- A flashy control panel doesn’t help if height range is wrong for transfers.
- Ignoring mattress compatibility
- Side rail safety and entrapment risk can change with the wrong mattress thickness or type.
- Choosing ICU beds for every ward
- Overspending reduces budget for mattresses, accessories, and spares that matter daily.
- Choosing manual beds where staff will crank constantly
- It increases workload and slows care routines.
- Not defining the specs tightly
- Vague tenders lead to substitutions that look similar but perform differently.
- Skipping training
- Misuse causes damage and safety incidents faster than most teams expect.
FAQ About Hospital Bed Types
1) Are Electric Hospital Beds always better than manual?
Not always. If patient needs are low and repositioning is rare, Manual Hospital Beds can work well. If staff adjust beds often, electric usually wins on safety and workflow.
2) Do ICU Hospital Beds follow different standards?
Many ICU beds still fall under recognized medical bed safety frameworks (often referencing IEC requirements), but the key is whether the specific bed is tested and documented for the functions you’re buying.
3) What’s the most important line in Medical Bed Specifications?
Safe working load + height range + rail/mattress compatibility. Those three affect daily safety and usability the most.
4) What should I request from a Hospital Bed Supplier before purchase?
Datasheets, test/conformity documentation, warranty terms, preventive maintenance plan, spare parts price list, and delivery/installation scope.
5) How do we reduce bed-related entrapment risk?
Follow recognized entrapment guidance, evaluate rail design and latching, and verify mattress fit and thickness for the bed system in use.
The best bed choice is the one that matches your care level: manual beds for low-acuity basics, electric beds for most inpatient rooms, and ICU beds where critical workflows demand advanced control and safety. When you compare Hospital Bed Types with clear specs, you protect patients, reduce staff strain, and avoid expensive replacements.
If you’re sourcing for a new ward, a clinic upgrade, or a full facility rollout, trust medi can support you with Healthcare Bed Solutions from defining Medical Bed Specifications to selecting the right Hospital Bed Manufacturer and arranging supply through a dependable Hospital Bed Supplier. Contact trust medi now to build a bed shortlist that fits your departments, budget, and safety requirements.